Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that affects the cervix, the lower part of the uterus (womb). It occurs when abnormal cells in the cervix grow and multiply uncontrollably, forming a tumor. Over time, the tumor can invade the surrounding tissues and spread to other parts of the body.
Early-stage cervical cancer often has no symptoms. However, as the cancer progresses, symptoms may include:
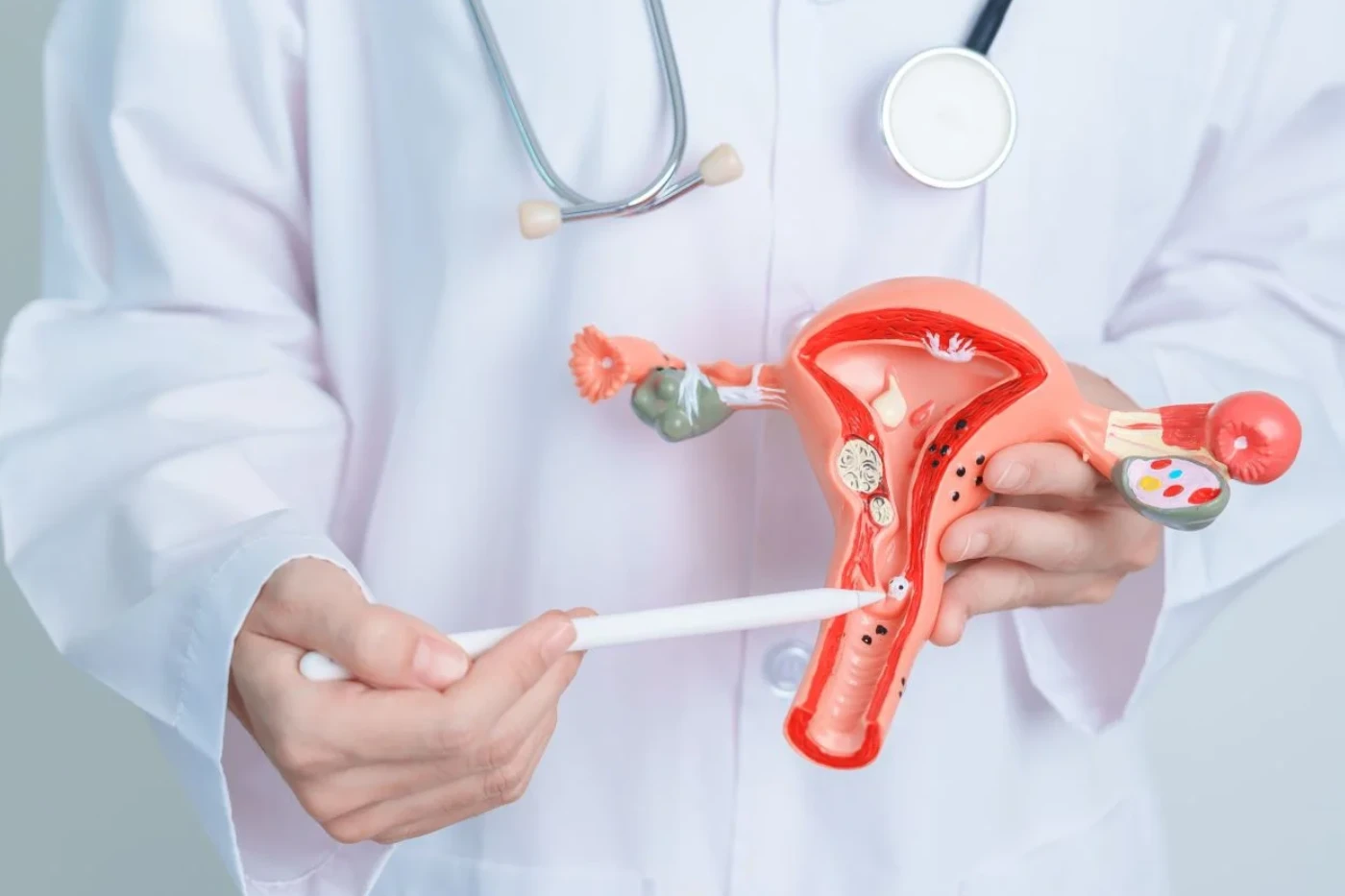

Women who have had sexual contact, have a weakened immune system, or have a history of cervical dysplasia (abnormal cell changes in the cervix) are at increased risk. Other risk factors include:
Diagnosis typically involves:


A Pap test, also known as a Pap smear, is a procedure to collect cells from the cervix to check for abnormal cell changes. The test can detect:
The main cause of cervical cancer is the human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is a common sexually transmitted infection that can cause genital warts and cervical cancer. There are over 100 types of HPV, but types 16 and 18 are most commonly associated with cervical cancer.
The goal of surgery is to remove the tumor, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterus to prevent the cancer from spreading.
Yes, cervical cancer can recur after treatment. Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments with a doctor are essential to detect any recurrences early.

The HPV test checks for the presence of HPV in the cervix. The test can detect:
Treatment options depend on the stage and aggressiveness of the cancer and include:
The goal of surgery is to remove the tumor and affected tissue to prevent the cancer from spreading. The type of surgery depends on the stage and location of the cancer.
The 5-year survival rate for cervical cancer is around 66%, depending on the stage and treatment. Early detection improves survival rates.
Yes, most women can resume normal activities after treatment. However, some may experience lingering effects like vaginal dryness or painful urination.

Early detection improves treatment outcomes and survival rates. It also reduces the risk of complications and improves quality of life. Regular screening and HPV vaccination can help prevent cervical cancer and detect it early, when it is most treatable.
Yes, cervical cancer can be prevented with:


Cancer Patients Treated
Our aim is to provide the best cancer treatment & care, make cancer care affordable and accessible to all. Provide cancer care without barriers viz financial, social, logistical, psychological etc. Latest Cancer Treatment based on evidence, delivered with empathy, with highest ethical standards.